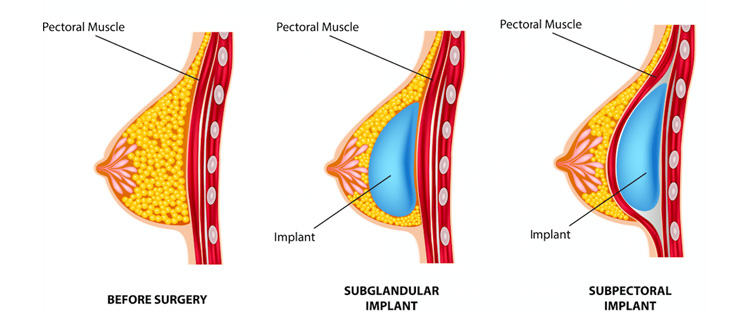
Breast implants placement
Over the muscle or behind the muscle ? In order to understand implants placement, patients need to know a few things about breast anatomy. Breast are made of several layers : the rib cage, the pectoral muscles, the mammary gland, the subcutaneous tissue and the skin.
A few options are available to breast augmentation patients regarding implants placement :
- The submuscular position (« under the muscle »).
- The subglandular position (« over the muscle »).
- A combination of these two positions : the dual plane technique (a portion of the implant is covered by the pectoral muscle while the other is not).
Breast implants positions : pros and cons
Subglandular placement pros
- The implant stays still when the pectoral muscle contracts (the result is natural) with no deformation.
- The procedure only causes low levels of pain or discomfort.
Subglandular placement cons
- There is a risk of implant contours being visible in skinny patients (a pinch test can assess this risk in the cleavage area).
- Implant rippling is also a risk with this position, which can be decreased by using silicone implants.
Submuscular placement pros
- The upper edge of the breast implant is covered by the muscle for a more natural looking cleavage.
- This position decreases the risk of capsular contracture.
Submuscular placement cons
- Breast shape changes when the pectoral muscle contracts.
- Postoperative pain is more significant than with subglandular placement but well tolerated by most patients.
- When the breasts are slightly sagging, the implant does not follow this motion because it is held in place by the muscle cover.
What about the dual plane placement ?
- The upper pole of the implant is well hidden behind the muscle, which offers a truly natural appearance of the cleavage.
- The lower part of the implant fills up the skin envelope nicely, which lifts up the areola slightly.
- This position offers a very natural evolution over time.
- Breast shape is only slightly affected by muscle contractions.
- The dual plane position causes less postoperative pain than the submuscular placement.





Laisser un commentaire